Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that can affect the tissues and organs in the head and neck area, including the mouth, throat, nose, sinuses, and salivary glands. These cancers can arise from various types of cells, including squamous cells, which line the surface of the skin and mucous membranes.
There are several different types of head and neck cancers, including:
This type of cancer affects the mouth, including the lips, gums, tongue, lining of the cheeks, and floor and roof of the mouth.
This type of cancer affects the back of the throat, including the base of the tongue, tonsils, and soft palate.
This type of cancer affects the nasopharynx, which is the upper part of the throat behind the nose.
This type of cancer affects the larynx, also known as the voice box, which is located in the neck.
This type of cancer affects the hypopharynx, which is the lower part of the throat.
This type of cancer affects the salivary glands, which are located in and around the mouth and produce saliva.
Studies have found that individuals with certain types of bacteria in their oral microbiome are at a higher risk for head and neck cancer. These bacteria, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum, have been found to promote inflammation and damage to the DNA in cells, which can lead to the development of cancer.
Additionally, poor oral hygiene and dental health can contribute to an imbalanced oral microbiome, leading to an increased risk of head and neck cancer. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing, can help maintain a healthy oral microbiome and reduce the risk of cancer.
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium that is commonly associated with periodontal disease, which is a severe form of gum disease, which is characterized by inflammation, destruction of gum tissue, and eventual loss of teeth if left untreated.
P. gingivalis is a rod-shaped bacterium that forms biofilms, which are complex communities of bacteria that adhere to surfaces, including teeth and gum tissue. This bacterium has the ability to evade the immune system and can produce a variety of virulence factors that contribute to its pathogenicity.
Some of the virulence factors produced by P. gingivalis include enzymes that degrade gum tissue, toxins that damage host cells, and molecules that modulate the host immune response.
Some studies have found an association between P. gingivalis and an increased risk of head and neck cancer. P. gingivalis has been detected in higher levels in tumor tissues of head and neck cancer patients compared to healthy individuals. P. gingivalis has been shown to promote inflammation, interfere with the immune response, and induce DNA damage, which may contribute to the development of head and neck cancer.
Moreover, P. gingivalis has been implicated in promoting cancer cell survival and proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis (programmed cell death), and promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), which are all hallmarks of cancer development and progression.

Fusobacterium nucleatum is a Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium that is commonly found in the human oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract. It is a pathogenic bacterium associated with various oral and systemic diseases, including periodontal disease, colorectal cancer, and intra-abdominal infections.
Fusobacterium nucleatum is known for its ability to adhere to and invade host cells, which contributes to its pathogenicity. It can also form biofilms, which are complex communities of bacteria that are attached to surfaces and can be difficult to remove. F. nucleatum is considered a "bridge organism" that can facilitate the colonization and growth of other pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity, contributing to the development of periodontal disease.
Research suggests that F. nucleatum may play a role in the development of and progression of head and neck cancer. F. nucleatum has been detected in higher levels in tumor tissues of head and neck cancer patients compared to healthy individuals. F. nucleatum has been shown to promote inflammation, disrupt the immune response, and stimulate cancer cell growth through various mechanisms, including the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and interaction with immune cells and other bacteria in the oral microbiome.
Moreover, F. nucleatum has been found to be associated with worse clinical outcomes in head and neck cancer patients, including increased tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and decreased overall survival. However, further research is needed to better understand the complex relationship between F. nucleatum and head and neck cancer, including the underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications.
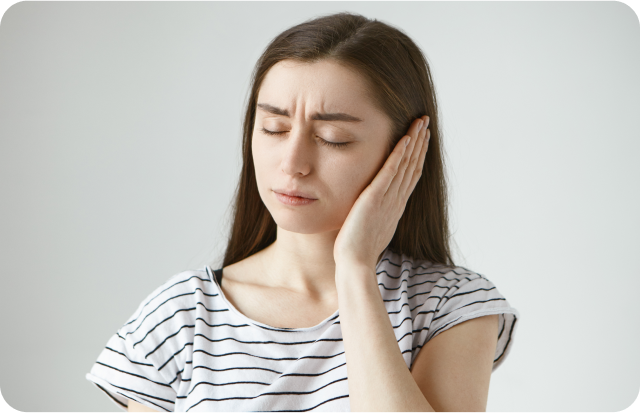


The symptoms of head and neck cancer can vary depending on the type and location of the cancer, but may include persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing or speaking, ear pain, hoarseness, and a lump or sore that does not heal. Treatment for head and neck cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches, depending on the stage and type of cancer. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene habits can also help reduce the risk of head and neck cancer.
The symptoms of head and neck cancer can vary depending on the type and location of the cancer, but may include persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing or speaking, ear pain, hoarseness, and a lump or sore that does not heal. Treatment for head and neck cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches, depending on the stage and type of cancer. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene habits can also help reduce the risk of head and neck cancer.
By addressing the connection between the oral microbiome and head and neck cancer, Dentulu is committed to providing comprehensive and proactive dental care to our patients.
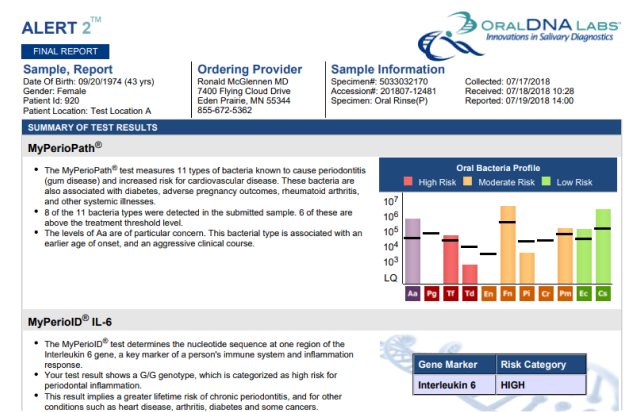
Generally, a salivary testing report will include the patient's identifying factors such as age, name, gender, and the date of the test. Next it will identify the testing results which could include inflammatory markers, oxidative stress markers, and genetic markers. Finally it will include a section on interpreting your results.
At Dentulu, we highly recommend each patient to schedule an appointment with their general dentist or primary care physician, or one of our highly trained Dentulu Teledentists who can discuss with you and assess your current dental and health conditions as well as prior health history to come up with the most appropriate care plan for your needs.
See Sample ReportIt’s simple! Click the link below, choose the package you'd like, follow the prompts, and have the kit delivered right to your door!
Once your test results come in, you can interpret the results yourself, follow up with your regular dentist, or schedule a consultation with one of our Dentulu Teledentists from your computer or mobile device at any time that is convenient for you!
 Interpreting Your Test Results
Interpreting Your Test Results
