Cardiovascular disease refers to a class of diseases that involve the heart and blood vessels. It is a broad term that encompasses various conditions affecting the cardiovascular system, including the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death worldwide and is often associated with risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, obesity, lack of physical activity, poor diet, and other lifestyle factors. There is also growing evidence to suggest that there is a link between the oral microbiome and cardiovascular disease. The oral microbiome is the collection of microorganisms that live in the mouth, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Some common types of cardiovascular disease include:
This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of fatty deposits called plaques. This can lead to reduced blood flow to the heart, which can result in chest pain (angina), heart attack, or other complications.
Also known as cerebrovascular disease, stroke occurs when the blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or blocked. This can happen due to a clot (ischemic stroke) or bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke), resulting in damage to brain tissue and potential long-term disability or death.
This condition happens when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to inadequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the body's organs and tissues. Heart failure can result from various underlying conditions such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or other heart disorders.
This refers to abnormal heart rhythms, which can include irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation), rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), or slow heartbeat (bradycardia). Arrhythmias can disrupt the normal functioning of the heart and may increase the risk of other cardiovascular complications.
This condition occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, typically the legs, become narrowed or blocked. It can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected limbs and may increase the risk of infections and ulcers.
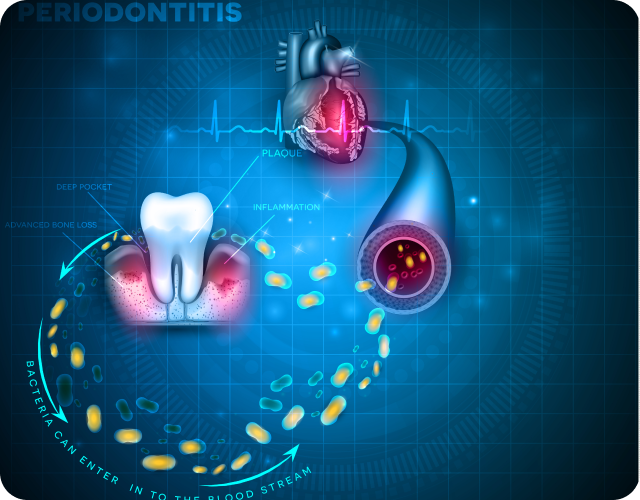
The oral microbiome, which consists of trillions of bacteria and other microorganisms in the mouth, has been found to have a connection to cardiovascular disease. Research has shown that the health of the oral microbiome can impact the health of the cardiovascular system, and there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that oral health plays a role in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease.
The oral microbiome and cardiovascular disease are connected through several mechanisms. One of the key factors is inflammation. Periodontal disease, a common oral condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums, has been linked to increased systemic inflammation in the body.

This chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque accumulates in the arteries, leading to narrowing and hardening of the arteries, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Furthermore, some specific bacteria found in the oral microbiome such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, have been implicated in the development of cardiovascular disease. These bacteria can enter the bloodstream through infected gums and promote inflammation and clotting, which can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
In addition to inflammation, the oral microbiome can also affect cardiovascular health through the production of certain chemicals. For example, some bacteria in the mouth can produce trimethylamine (TMA), which is converted by the liver into trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). TMAO has been associated with increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events, as it can promote plaque formation in the arteries.

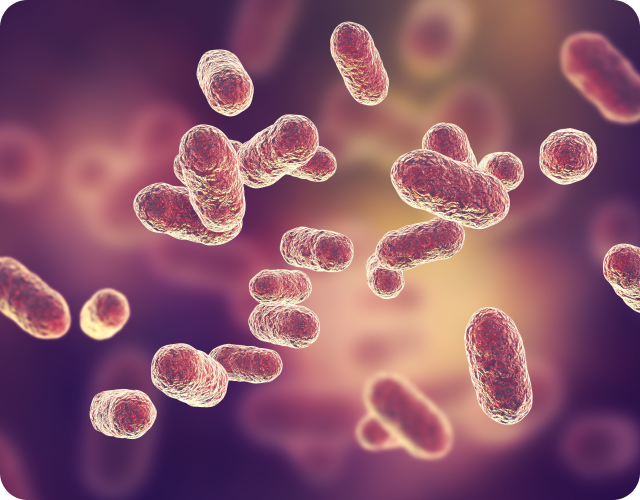
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium that is commonly associated with periodontal disease, which is a severe form of gum disease, which is characterized by inflammation, destruction of gum tissue, and eventual loss of teeth if left untreated. P. gingivalis is a rod-shaped bacterium that forms biofilms, which are complex communities of bacteria that adhere to surfaces, including teeth and gum tissue.
This bacterium has the ability to evade the immune system and can produce a variety of virulence factors that contribute to its pathogenicity. Some of the virulence factors produced by P. gingivalis include enzymes that degrade gum tissue, toxins that damage host cells, and molecules that modulate the host immune response.
Research has shown that P. gingivalis is not only associated with oral health problems but also has been implicated in systemic health issues. Studies have suggested that P. gingivalis may be involved in the development of various systemic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, due to its ability to enter the bloodstream from the oral cavity and spread to other parts of the body.
In particular, P. gingivalis has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease by promoting inflammation, contributing to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques (fatty deposits) in arteries, and interfering with blood clotting mechanisms. Additionally, P. gingivalis has been found in atherosclerotic plaques in arteries, indicating a potential role in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease.

It's important to note that maintaining good oral health and a healthy oral microbiome may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, as well as a healthy diet and lifestyle, can all contribute to a healthy oral microbiome and overall cardiovascular health. Furthermore, regular dental check-ups and screenings for gum disease can help detect and address any oral health issues early, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. At Dentulu, we recognize the important connection between oral health and overall health, including cardiovascular health. Our licensed dentists are trained to provide comprehensive oral care, including addressing gum health and providing education on maintaining a healthy oral microbiome. Through our teledentistry platform, patients can access convenient and accessible dental care to support their oral and overall health. Contact us today to learn more about how Dentulu can help you maintain a healthy smile and a healthy heart.

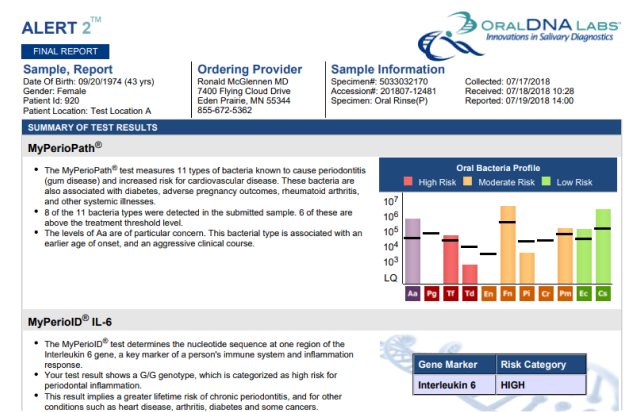
Generally, a salivary testing report will include the patient's identifying factors such as age, name, gender, and the date of the test. Next it will identify the testing results which could include inflammatory markers, oxidative stress markers, and genetic markers. Finally it will include a section on interpreting your results.
At Dentulu, we highly recommend each patient to schedule an appointment with their general dentist or primary care physician, or one of our highly trained Dentulu Teledentists who can discuss with you and assess your current dental and health conditions as well as prior health history to come up with the most appropriate care plan for your needs.
See Sample ReportIt’s simple! Click the link below, choose the package you'd like, follow the prompts, and have the kit delivered right to your door!
Once your test results come in, you can interpret the results yourself, follow up with your regular dentist, or schedule a consultation with one of our Dentulu Teledentists from your computer or mobile device at any time that is convenient for you!
 Interpreting Your Test Results
Interpreting Your Test Results
